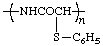
poly{imino[1-oxo-2-(phenylsulfanyl)ethylene]}
(heteroatom is senior to acyclic carbon chain; in the chain the substituent earlier in the alphabetical order has a lower locant; Rules 1, 10e)
Continued with 9. Examples of Polymer Names 41-60
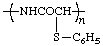
poly{imino[1-oxo-2-(phenylsulfanyl)ethylene]}
(heteroatom is senior to acyclic carbon chain; in the chain the substituent earlier in the alphabetical order has a lower locant; Rules 1, 10e)
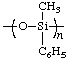
poly{oxy[methyl(phenyl)silanediyl]} or poly[methyl(phenyl)siloxane]
(for an alternative name, see [ref 10])
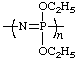
poly[nitrilo(diethoxy-λ5-phosphanetriyl)] or poly(diethoxyphosphazene)
(N is senior to P; Rule 4; for an alternative name, see [ref 10])
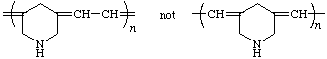
poly(piperidine-3,5-diylideneethanediylidene)
(piperidine ring is senior to acyclic carbon chain; Rule 1)
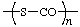
poly(sulfanediylcarbonyl)
(S is senior; Rule 1)
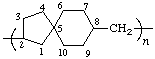
poly(spiro [4.5]decane-2,8-diylmethylene)
(ring system is senior to acyclic carbon chain; Rules 1, 12)
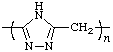
poly(4H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diylmethylene)
(heterocycle is senior to acyclic carbon chain; Rules 1, 12)
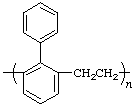
poly[(2-phenyl-1,3-phenylene)ethylene]
(ring system is senior to acyclic carbon chain; Rules 1, 12, 18)
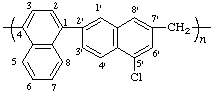
poly[(5'-chloro[1,2'-binaphthalene]-4,7'-diyl)methylene]
(ring system is senior to acyclic carbon chain; Rules 1, 9c, 12Rules 1, 9c, 12)
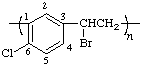
poly[(6-chlorocyclohex-1-ene-1,3-diyl)(1-bromoethylene)]
(ring is senior to acyclic carbon chain; lower free-valence locant on the left; lower locant for Br in ethylene; Rules 1, 9c, 10d, 11)
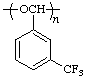
poly(oxy{[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]methylene})
(O is senior to methylene; Rule 1)
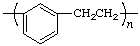
poly(1,3-phenyleneethylene)
(ring is senior to acyclic carbon chain; Rule 1, 11)
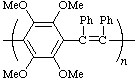
poly[(tetramethoxy-1,4-phenylene)(1,2-diphenylethene-1,2-diyl)]
(ring is senior to acyclic carbon chain; Rule 1)
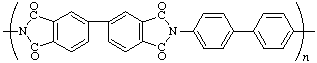
poly{(1,1',3,3'-tetraoxo[5,5'-biisoindoline]-2,2'-diyl)biphenyl-4,4'-diyl}
(heterocyclic system is senior to carbocyclic system; Rule 1, 3c, 12)
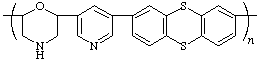
poly(morpholine-2,6-diylpyridine-3,5-diylthianthrene-2,8-diyl)
(nitrogen heterocycles are senior to non-nitrogen heterocycle; ring with larger number of heteroatoms is senior; Rules 2a, 2e, 12)
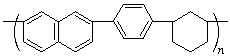
poly(naphthalene-2,7-diyl-1,4-phenylenecyclohexane-1,3-diyl)
(two-ring system is senior to single-ring systems; benzene as least hydrogenated is senior to cyclohexane; Rules 8a, 9a, 11, 12)
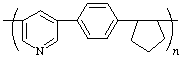
poly(pyridine-3,5-diyl-1,4-phenylenecyclopentane-1,2-diyl)
(heterocycle is senior to carbocycles; larger carbocycle is senior to smaller; Rules 1, 8b, 11, 12)
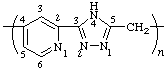
poly(pyridine-4,2-diyl-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diylmethylene)
(heterocycles are senior to acyclic carbon chain; larger nitrogen ring; Rules 1, 2d, 12)
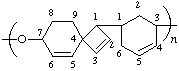
poly(oxyspiro [3.5]nona-2,5-diene-7,1-diylcyclohex-4-ene-1,3-diyl)
(O is senior; shorter path to the senior ring system; Rules 1, 8a, 11, 12)
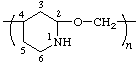
poly(piperidine-4,2-diyloxymethylene)
(heterocycle is senior to heteroatom; shorter path between them; Rules 1, 12)
10. IUPAC. "Nomenclature for regular single-strand and quasi-single-strand inorganic and coordination polymers 1984", Pure Appl.Chem. 57, 149-168 (1985).Reprinted as Chapter 6 in IUPAC. Compendium of Macromolecular Nomenclature, Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford (1991) (PDF) and as Chapter II-7 in IUPAC. Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry II, Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge (2001).